Superfund Research Program
NIEHS does not maintain articles more than three years. Older articles are stored on our archive site. Click this link to go to the NIEHS website archive for News Stories. In the archive, you may encounter broken links, images, or videos in some articles.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - June 20, 2024
New approaches to address the occupational health and safety risks found in various workplaces were the focus of a Superfund Research Program (SRP) Progress in Research webinar series.
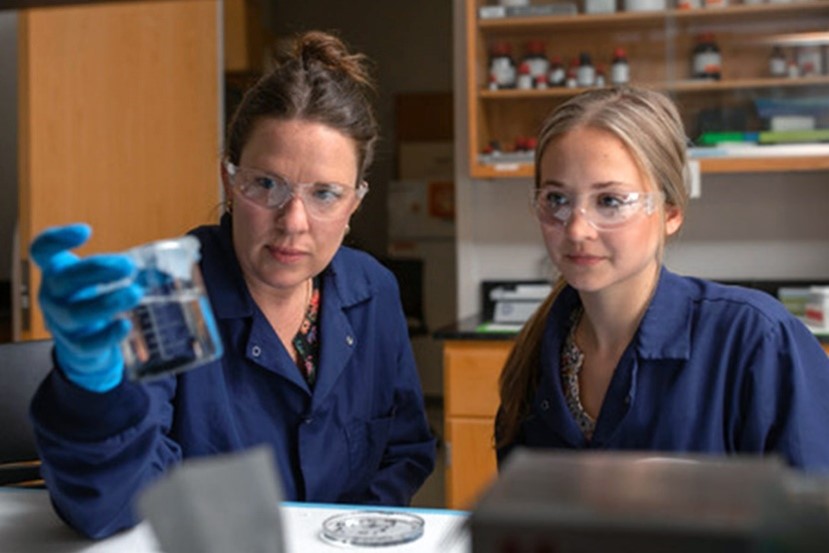

Science Highlights - June 17, 2024
Researchers at the University of Kentucky (UK) Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center tested the impact of electrically charging certain filtration materials to remove PFAS.

Paper of the Month - June 17, 2024
Texas A&M University SRP Center researchers evaluated the ability of six different sorbent materials, made up of activated carbon or specialized clays, to trap four PFAS chemicals in soil. They exposed worms and aquatic plants to soil or water to measure the bioavailability of PFAS and how changes in bioavailability translate to toxicity.

Paper of the Month - June 17, 2024
Scientists at the University of Arizona SRP Center examined the effects of arsenic, cadmium, ferrihydrite, and pepsin, an enzyme responsible for protein digestion. Scientists used a simulated gastrointestinal (GI) tract to measure bioaccessibility, or the amount of toxic metals that could be released during digestion and absorbed into the blood stream.

Paper of the Month - June 17, 2024
A study led by a team at the Northeastern University SRP Center examined the relationship between exposure to an herbicide before birth and neurodevelopment in young children. Researchers assessed herbicide exposure of 143 mother-baby pairs from Puerto Rico by collecting urine samples from the mothers during pregnancy and measuring levels of glyphosate and breakdown product of herbicide.

Paper of the Month - May 7, 2024
A new approach might help scientists better prioritize which PFAS, a large class of compounds linked to negative health outcomes, should be included in health risk assessments, according to researchers at the Texas A&M University Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center.

Paper of the Month - May 7, 2024
Researchers at the University of Iowa Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center used biochar, a carbon rich byproduct of burning plant matter, and bacteria to clean up polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in aquatic environments.

Outreach and Community Engagement - May 6, 2024
NIEHS-funded researchers at the University of Iowa and the North Carolina State University (NC State) Superfund Research Program (SRP) centers partnered to address community concerns about polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) discovered in an NC State building. During an online forum on February 24, 2024, the team answered questions from the NC State community about the health effects of PCBs.
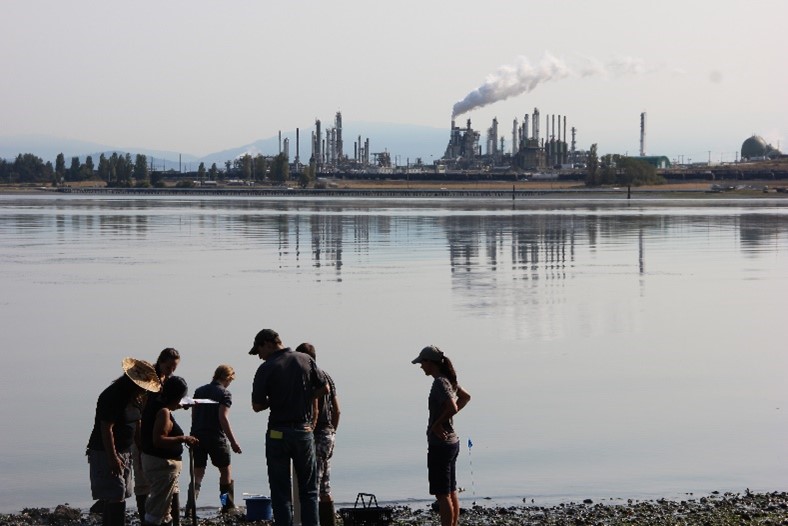

Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 17, 2024
Jamie Donatuto, Ph.D., is in a unique position as both the environmental health analyst for the Swinomish Indian Tribal Community and as the co-leader of the Community Engagement Core at the Oregon State University Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center. She has spent decades researching the intersections of environmental contaminant exposures, Indigenous practices, and community health, and she regularly advocates for and educates others about ethical research collaborations that benefit Tribal health.

Outreach and Community Engagement - April 12, 2024
Researchers at the NIEHS-funded Duke University Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center are using outreach and community-engaged research to help North Carolina residents identify, understand, and manage risks related to soil contamination. Center staff also develop a variety of tools to help residents identify contaminant sources near their gardens.
Outreach and Community Engagement - April 11, 2024
Many NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded scientists and trainees, as well as SRP staff, attended the 63rd Annual Meeting and ToxExpo for the Society of Toxicology (SOT), held March 10-14 in Salt Lake City.
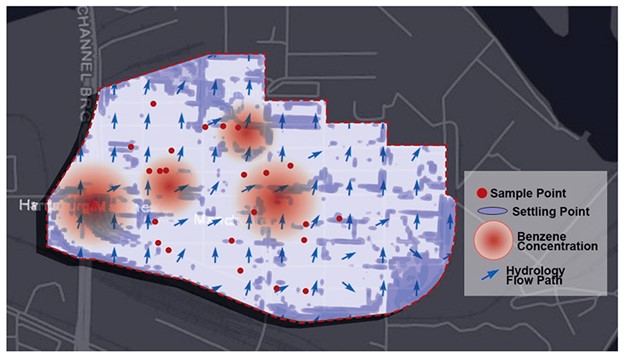
Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 11, 2024
As head of the Department of Landscape Architecture and Urban Planning and a member of the NIEHS-funded Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center at Texas A&M University, Galen Newman, Ph.D., focuses on improving urban resilience against natural disasters, such as hurricanes and flooding. His work shapes community resilience plans that use environmentally conscious landscape design to improve health outcomes.
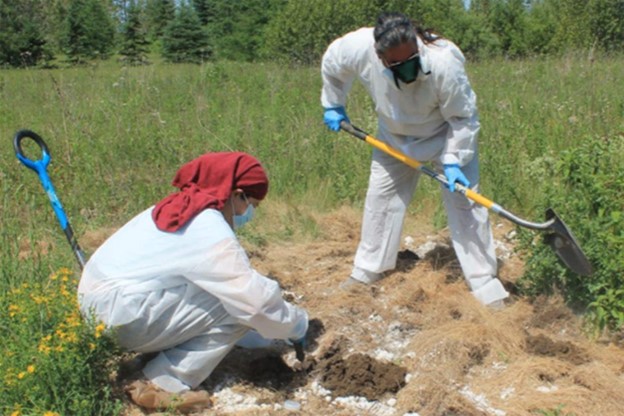

Outreach and Community Engagement - April 11, 2024
Scientists supported by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) together with community and Mi kmaq Nation tribal members are using plants to remove PFAS from a contaminated site in northern Maine, a technique known as phytoremediation.

Paper of the Month - March 22, 2024
A new approach developed by researchers at the University of New Mexico Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center combines limestone and a bone-like mineral called hydroxyapatite to remove arsenic and uranium from water.

Outreach and Community Engagement - March 15, 2024
Researchers at the Louisiana State University (LSU) Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center used community interview data, referred to as oral history, to reveal long-term effects of a thermal treatment waste facility on residents in Colfax, Louisiana.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - March 7, 2024
As the community engagement coordinator at the University of North Carolina at Chapell Hill (UNC) Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center, Andrew George, Ph.D., is educating rural communities about the health risks of drinking well water contaminated with metals. He also relies on partnerships with community organizations across North Carolina to help under-resourced communities test their wells for free.
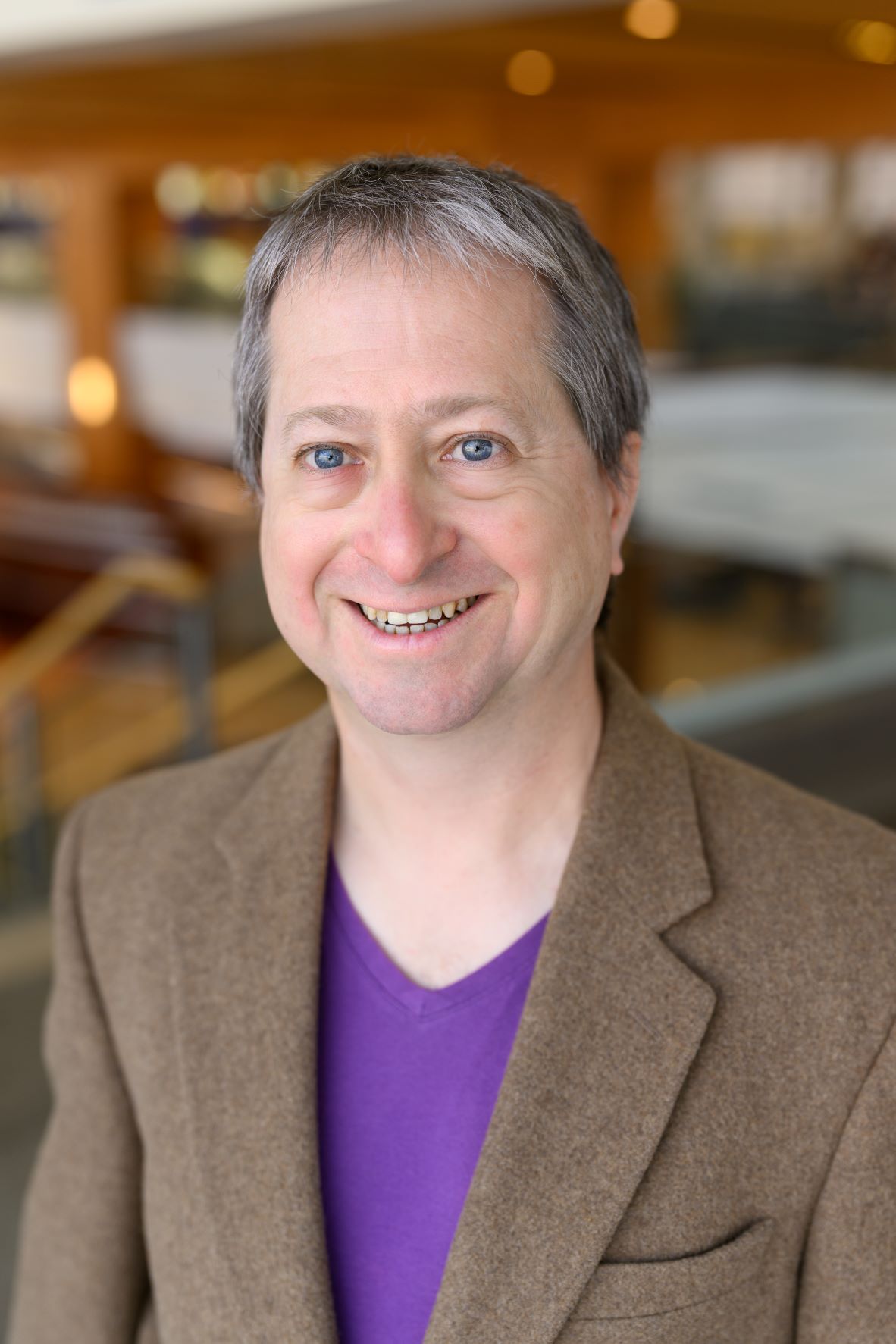

Science Highlights - February 14, 2024
Researchers from the University of Kentucky (UK) SRP Center are using machine learning techniques to help interpret how chemicals are processed, or metabolized, in the body. A series of interconnected processes in the body, known as metabolic pathways, can convert substances into smaller molecules, or metabolites. For certain chemicals, these metabolites can be more toxic than their parent compound.

Paper of the Month - February 14, 2024
A new approach developed by Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded researchers improved the ability of carbon-based filters to remove arsenic from drinking water. This method, which is inspired by a cooking technique known as sous vide, may offer a cheaper and more practical solution to prevent arsenic exposure.

Paper of the Month - February 14, 2024
Researchers at the North Carolina State University Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center and small business collaborators developed a new approach that combines advanced imaging methods with machine learning to rapidly image and count neutrophils, a type of immune cell, in zebrafish embryos. Research suggests that exposure to environmental pollutants can decrease neutrophil levels, emphasizing the need for strategies to screen chemicals affecting neutrophil counts.
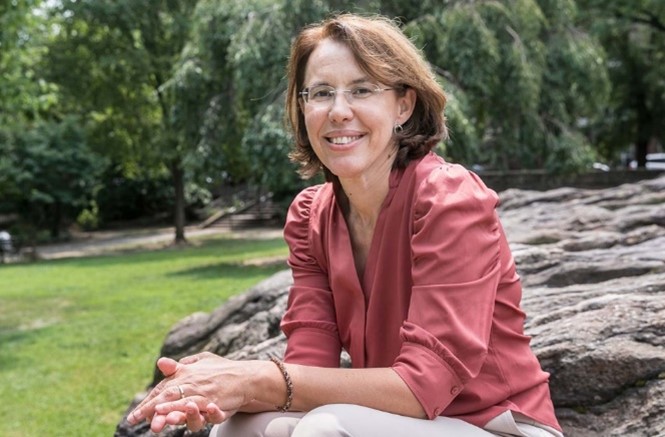

Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 14, 2024
Ana Navas-Acien, M.D., Ph.D., grew up in a desert-like area of Spain called Almeria where drinking water was scarce. For years, her parents relied on a rainwater collection system called an aljibe for drinking and cooking. These early experiences planted a seed.
Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 14, 2024
Superfund Research Program (SRP) grant recipient Robyn Tanguay, Ph.D., was recently interviewed by NIEHS Director Rick Woychik, Ph.D. Tanguay, who serves as the director of the Oregon State University SRP Center, discussed her research using zebrafish and why she thinks they represent a paradigm shift in toxicological research.
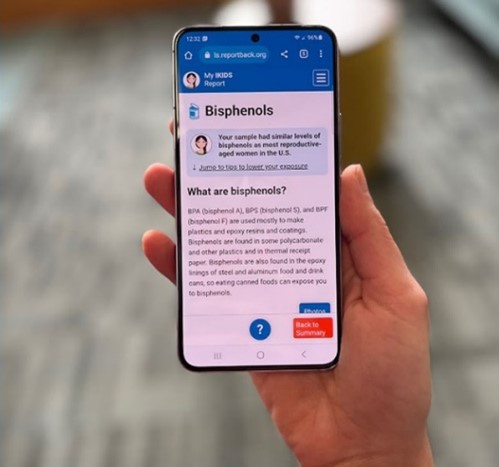
Outreach and Community Engagement - February 14, 2024
NIEHS-funded researchers have created a new framework designed to help scientists report back study findings about potential exposures to participants. The 12-point framework, developed by Katrina Korfmacher, Ph.D., and Julia Brody, Ph.D., of the Northeastern University PROTECT Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center, aims to make report-back a routine part of research within the environmental health sciences.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - January 22, 2024
While Jennifer Richmond-Bryant, Ph.D., was studying for a degree in civil and environmental engineering at Cornell University, she heard that workers in nearby municipal offices were experiencing "sick building syndrome." This experience highlighted for her that environmental issues were really health issues.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - January 22, 2024
Prior to joining the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 2005 as a community engagement and education specialist, Kathleen Vandiver, Ph.D., taught middle school science for 16 years.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - January 22, 2024
The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) selected Rollie Mills, from the University of Kentucky (UK) SRP Center, as the 26th recipient of the Karen Wetterhahn Memorial Award.

Outreach and Community Engagement - January 22, 2024
The annual grant recipient meeting of the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP), held Dec. 4-6 in Albuquerque, New Mexico, showcased how collaborative research can accelerate scientific discovery to protect the health of communities exposed to harmful contaminants.
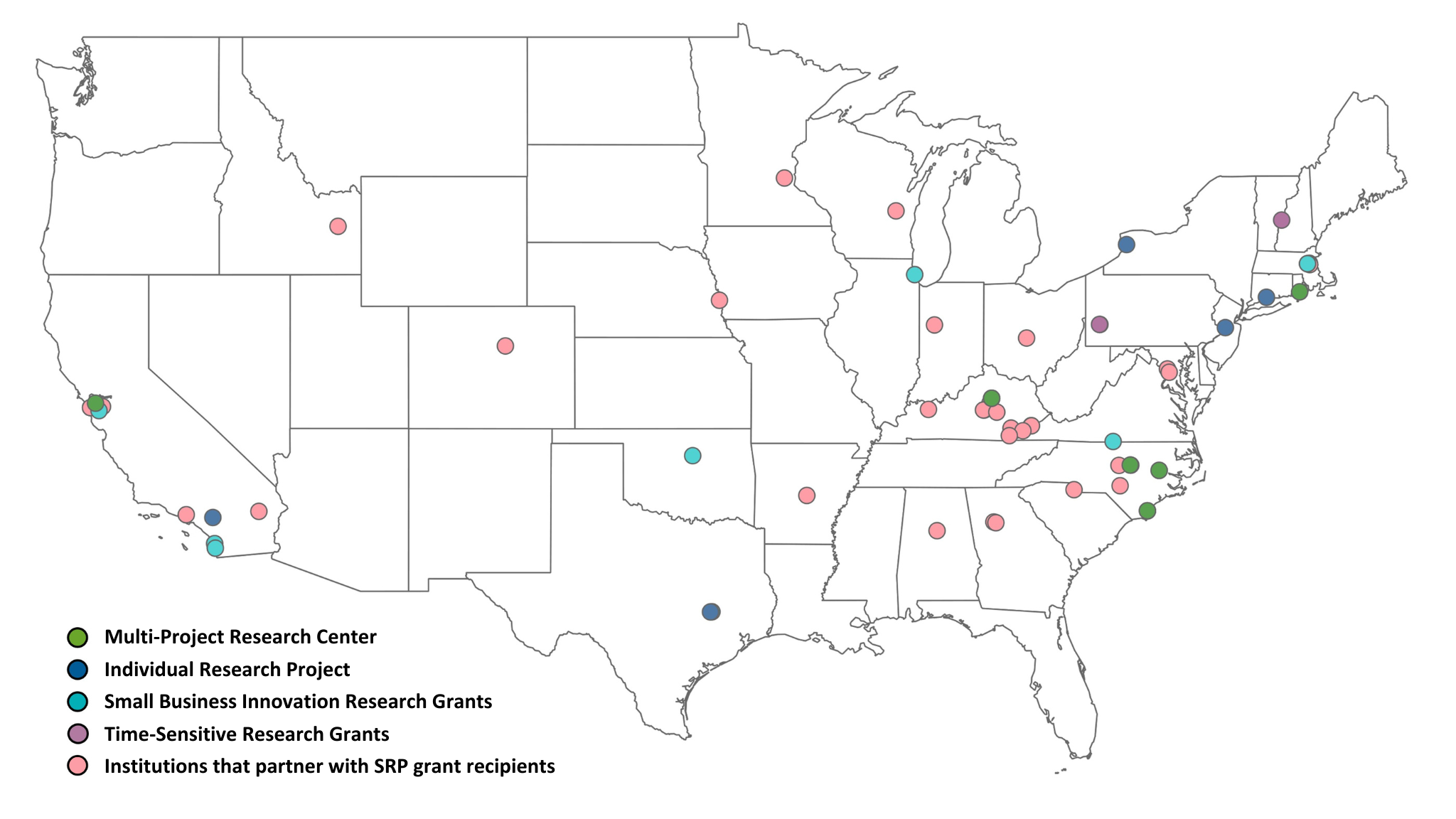
Grant Recipient Spotlights - January 3, 2024
The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) recently brought together several grant recipients and experts from other federal agencies to discuss new strategies and continuing challenges for PFAS site characterization. The three-session event, Tools for PFAS Site Characterization, included presentations on research efforts and tool development for sampling, monitoring, detecting, and characterizing PFAS. The widespread commercial use and the variety of risks of PFAS make site characterization important to researchers, who need to know which PFAS chemicals are where.
Science Highlights - December 7, 2023
A team of scientists funded by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) published a new workflow to help researchers across disciplines share environmental health data more effectively. The workflow provides a standardized framework for collecting, organizing, and distributing scientific data so that it can be more easily understood and used by other groups.

Paper of the Month - December 7, 2023
A study funded by SRP, at the University of California, Riverside, revealed important mechanistic information about how some microbes break down PFAS in the environment. The findings may inspire more cost-effective bioremediation approaches.

Paper of the Month - December 7, 2023
NIEHS-funded researchers developed a new approach to improve how environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs) are generated and studied in the lab at the Louisiana State University SRP Center. This strategy addresses a deficiency in methods to simulate realistic environmental exposures in animals.

Science Highlights - December 7, 2023
Members of the Federal Remediation Technologies Roundtable convened November 7 to share approaches for sampling and characterizing sites polluted by PFAS, a class of harmful chemicals that resist degradation. Through several case studies, speakers also illustrated unique challenges to understanding the sources and extent of PFAS contamination in the field.
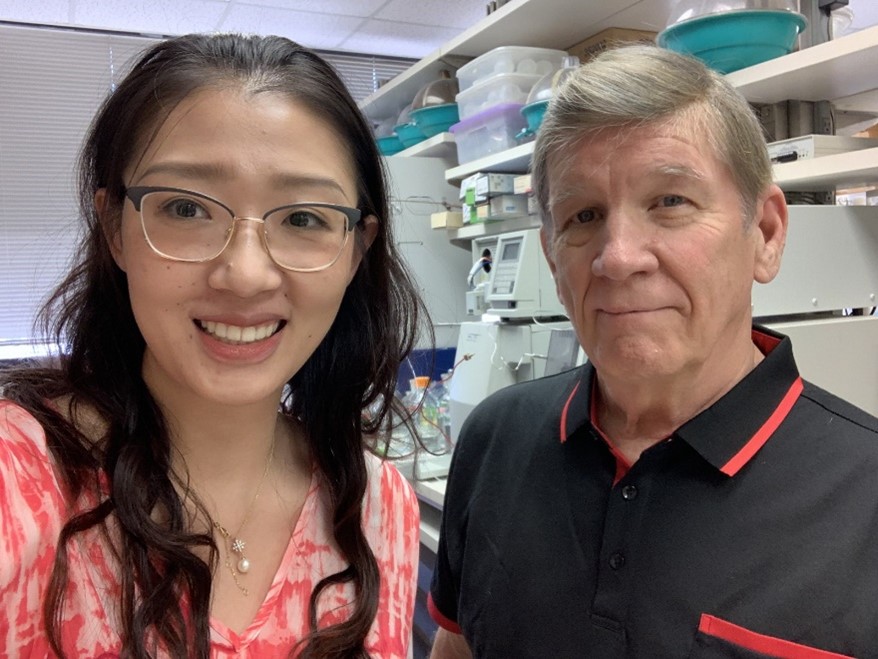

Science Highlights - November 17, 2023
Texas A&M University scientists developed a skin cream that may protect people from contaminants in floodwaters, such as benzene, toluene, and xylene. The cream, which forms a barrier between human skin and contaminants, is the culmination of several studies, partially funded by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP), which have explored materials that can adsorb and immobilize toxicants to reduce human exposures.

Paper of the Month - November 17, 2023
Chemical emissions from flooring can predict polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) concentrations in room air, according to NIEHS-supported research. The findings could inform targeted remediation strategies for indoor spaces.

Outreach and Community Engagement - November 9, 2023
Two core goals of multi-project NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) centers are community engagement and research training. Summer programs provide opportunities for center researchers and trainees to serve as mentors and share their work with the community and for students of all ages, from elementary school to college, to learn more about environmental health and research.
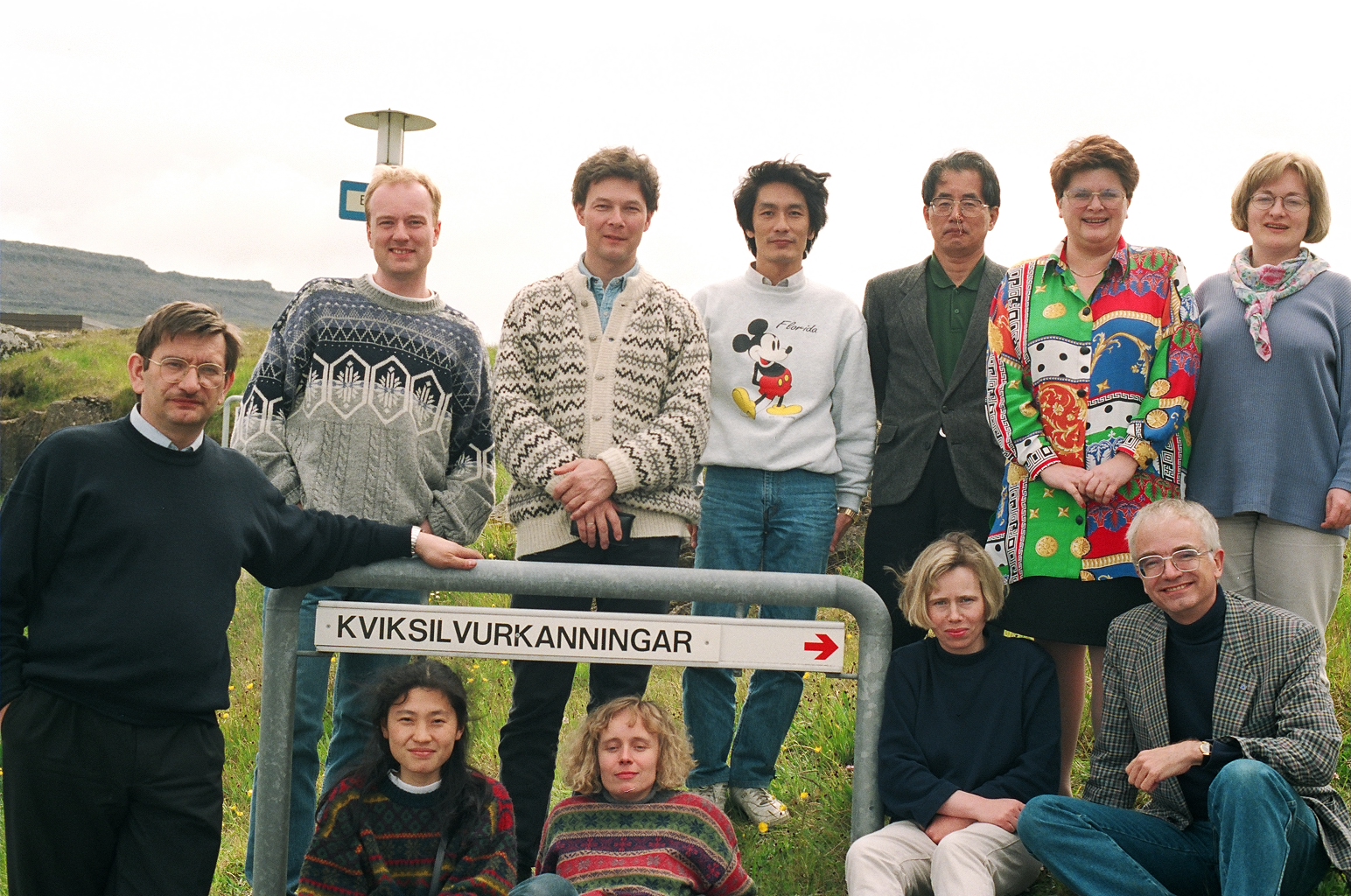

Grant Recipient Spotlights - October 20, 2023
Longtime NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) grant recipient Philippe Grandjean describes what kickstarted his career and where his research is headed, as well as the health effects of PFAS and how people can limit their exposure. Grandjean is an investigator at the University of Rhode Island SRP Center and works with communities in the Faroe Islands, an archipelago between Iceland and Norway.

Paper of the Month - October 20, 2023
NIEHS-funded researchers with the Columbia University SRP Center identified metals that were associated with biological age acceleration, where exposure may be a risk factor for aging-related diseases in Native American communities. Although metal exposure may speed age acceleration, exposures are preventable, and the authors findings provide an additional strategy to prevent premature mortality.

Paper of the Month - October 20, 2023
Scientists with North Carolina State University SRP Center measured levels of PFAS in dogs, horses, and children in towns downstream of a PFAS manufacturing plant after the community voiced concern about the health of their pets and families. The authors identified concentrations of two types of PFAS in dogs that were similar to the concentrations found in children from another North Carolina town.

Paper of the Month - October 20, 2023
Texas A&M University SRP Center researchers deployed a mobile air monitoring van in East Palestine, Ohio, following a train derailment. The van contained real-time, highly sensitive instrumentation to perform air quality analysis, and was driven around locations up- and down-wind of the train derailment for two days.

Outreach and Community Engagement - October 20, 2023
Researchers funded by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) describe reasons for water contamination disparities, identify current private well disparities, and review how community engagement and interventions like pitcher filters can help protect marginalized communities.
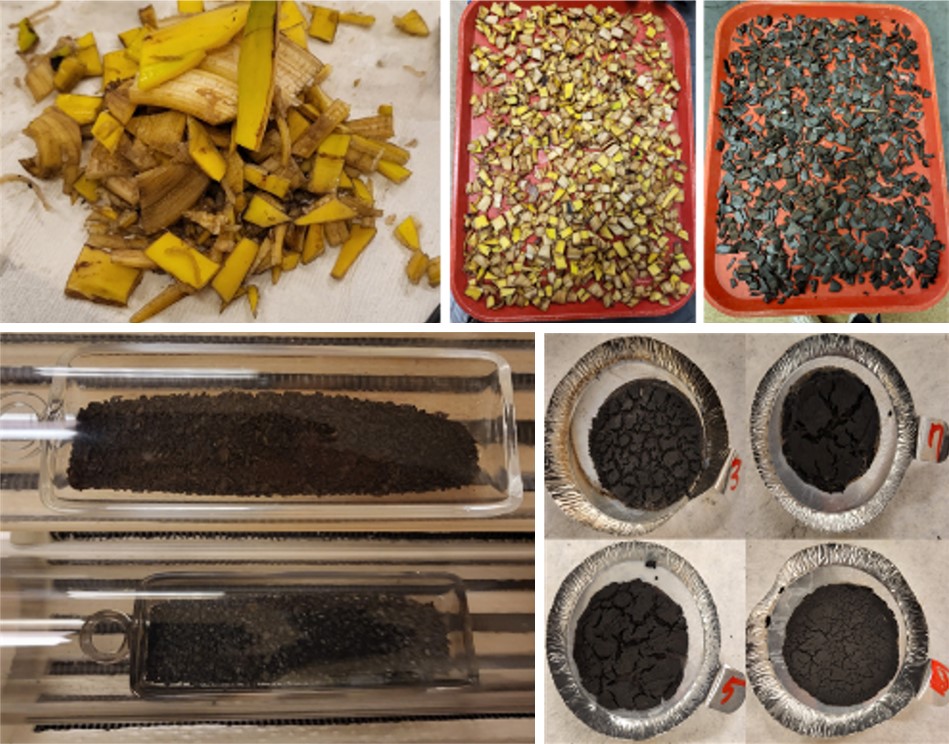

Science Highlights - October 6, 2023
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded researchers explored a new, cost-effective method of water treatment using biochar - a conductive, absorbent material - made from banana peels. This approach could inform large-scale, low-cost treatments in water systems, according to the authors at the Northeastern University Puerto Rico Testsite for Exploring Contamination Threats (PROTECT) SRP Center.

Outreach and Community Engagement - October 6, 2023
Monica D. Ramirez-Andreotta, Ph.D., at the University of Arizona SRP Center is interviewed by Ashley Ahearn for the NIEHS podcast where she discusses the role and impacts of participatory research.

Science Highlights - September 11, 2023
How the body repairs DNA damage following exposure to a chemical called N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) can provide new insights for cancer treatment, according to Jennifer Kay, Ph.D. The former Massachusetts Institute of Technology SRP Center trainee presented her findings during the August 1 Wetterhahn Award Seminar.

Paper of the Month - September 11, 2023
A federal regulation lowering the amount of arsenic allowed in public water systems reduced arsenic exposure among communities across the U.S., found researchers at the Columbia University Northern Plains SRP Center.

Science Highlights - September 11, 2023
A new report released by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine provides recommendations for implementing new approach methodologies (NAMs) in human health risk assessments. The committee that developed the report, which was sponsored by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), included several SRP grant recipients.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 7, 2023
Johnnye Lewis, director of the University of New Mexico Superfund Research Center, researches the Tribal health implications of exposures to environmental pollutants, particularly those from hardrock mining activity.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 7, 2023
As a high schooler, Kelly Pennell, Ph.D., was inspired by environmental and human rights activist Ken Saro-Wiwa to help people affected by environmental exposures. Now, as director of the University of Kentucky (UK) Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center, she is working to protect public health from exposures to toxic substances like PFAS, trichloroethylene (TCE), and tetrachloroethene (PCE).

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 1, 2023
Led by Northeastern University and funded by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP), the Puerto Rico Test Site to Explore Contamination Threats (PROTECT) SRP Center brings together researchers from many institutions to explore the connection between environmental exposures and preterm birth in Puerto Rico.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - August 7, 2023
Seven NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) trainees won K.C. Donnelly Externship Award Supplements to conduct research outside of their host centers. The three-month-long externships provide current SRP-funded graduate students and postdoctoral researchers the opportunity to learn new methods and techniques, while working in other SRP-funded institutions and government labs.

Paper of the Month - August 4, 2023
Researchers partly funded by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) identified key changes in placental gene expression that are associated with the development of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children born preterm. The study was led by a team at the University of Carolina at Chapel Hill SRP Center.

Science Highlights - August 4, 2023
With funding from the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) and other NIEHS programs, researchers at the Oregon State University (OSU) SRP Center developed a simple, non-invasive approach to monitor personal chemical exposures using silicone wristbands. The highly sensitive wristbands can be used to measure exposure to low levels of hundreds of chemicals, offering a unique tool to better understand the complex mixtures people may be exposed to throughout daily life.

Paper of the Month - August 4, 2023
Prenatal exposure to benzene may predispose offspring to metabolic diseases later in life, according to a study in mice. Partly funded by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP), the study was led by researchers at the Wayne State University SRP Center.
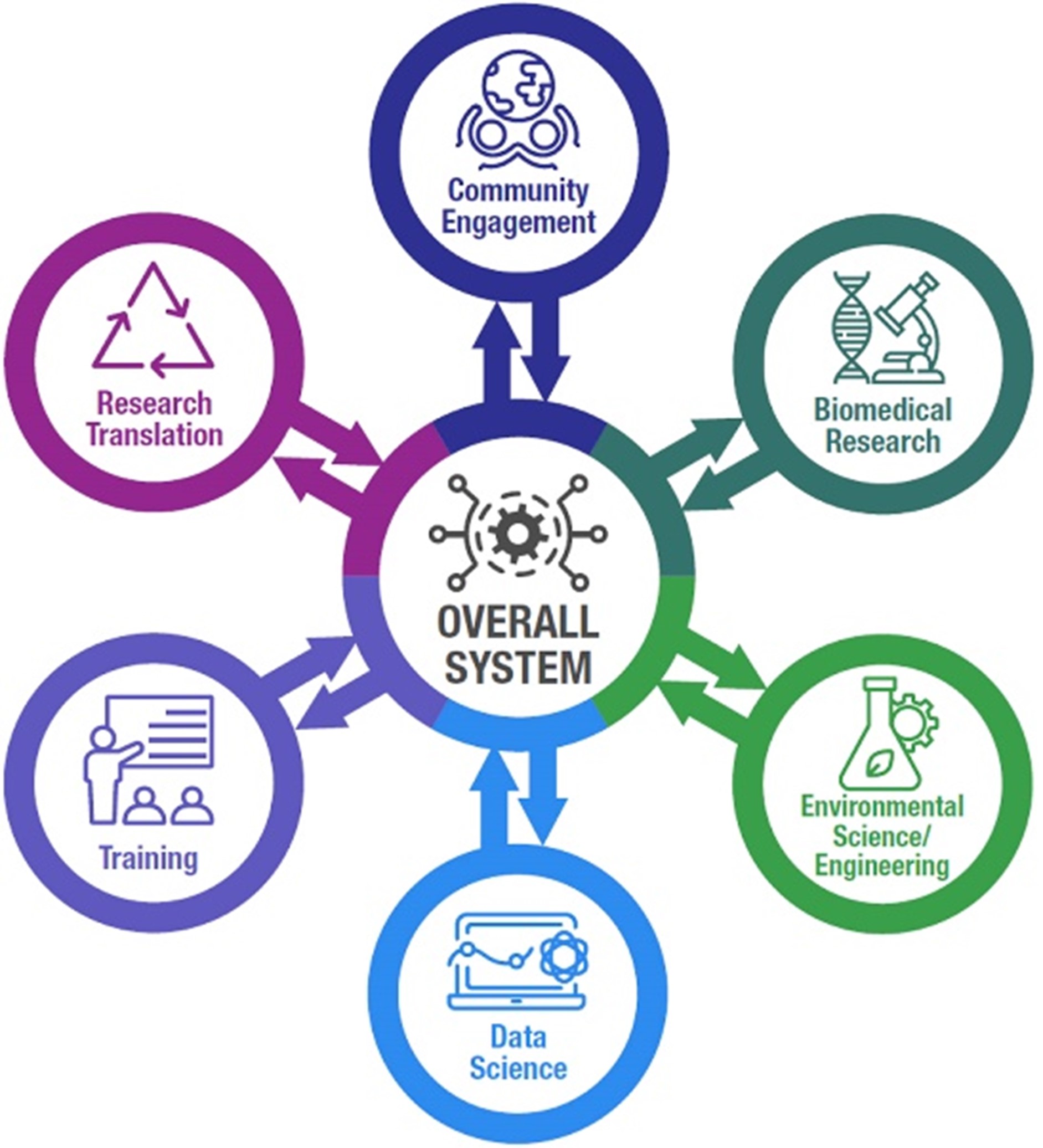
Science Highlights - July 6, 2023
Current and upcoming research to address complex environmental health issues related to hazardous contaminants, climate-related disasters, and more, headlined the recent NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) Progress in Research webinar series. Over the course of four sessions in April and May, the series highlighted 11 new and renewed SRP multiproject centers funded in 2022.

Paper of the Month - July 6, 2023
Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl (PFAS) can hinder dieting efforts to lose weight, according to a study by the University of Rhode Island SRP Center. PFAS, which are found in numerous industrial and consumer products, have been linked to various health problems, including metabolic changes and obesity.
Science Highlights - June 21, 2023
Researchers with the NIEHS-funded Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center have found distinctive genetic patterns signifying damage from the toxic chemical N-nitrosodimethylamine, or NDMA. The patterns could potentially be used to monitor cancer development and inform therapeutic interventions.

Paper of the Month - June 2, 2023
Researchers at the University of California, Davis SRP Center developed a DNA-based sensor that can detect trace amounts of organophosphate pesticides in food products.

Science Highlights - June 2, 2023
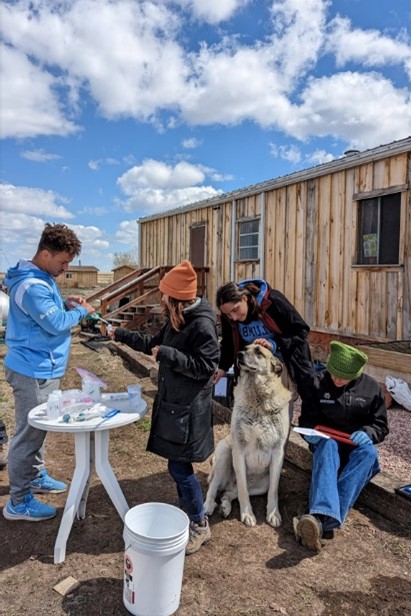
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded researchers recently installed filtration systems in Native American communities to reduce exposure to and the health effects of arsenic-contaminated drinking water. Led by the Columbia University Northern Plains SRP Center and in partnership with Northern Plain Tribal Nations and the Indian Health Service, the team installed arsenic filters under household kitchen sinks and launched a corresponding educational campaign.

Paper of the Month - June 2, 2023
Environmental factors, such as ultraviolet (UV) light, can alter the chemistry of miniscule plastic fragments, potentially increasing their toxicity on lung cells, according to a University of New Mexico SRP Center study.

Paper of the Month - June 2, 2023
SRP-funded small business Weaver Labs developed a novel technology to clean up water contaminated with PFAS. Their materials can be reused multiple times and are potentially less expensive than current remediation technologies, the authors said.

Outreach and Community Engagement - June 1, 2023
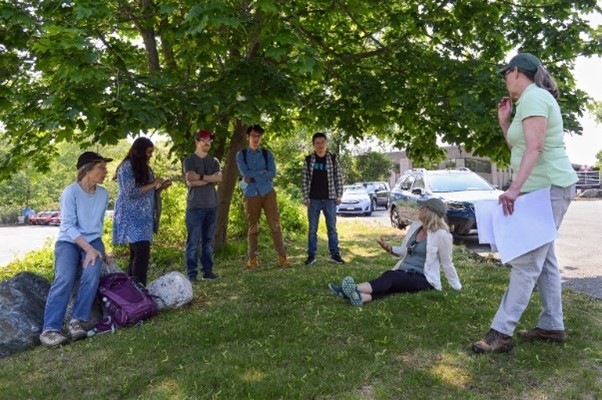
NIEHS-funded researchers recently developed a new online course to aid concerned residents and other community members through the process of cleaning up environmental contamination. The course includes educational and interactive modules, short videos, and questions for reflection to help guide participants to identify and address chemical exposures in their homes, neighborhoods, and local communities.

Outreach and Community Engagement - May 18, 2023
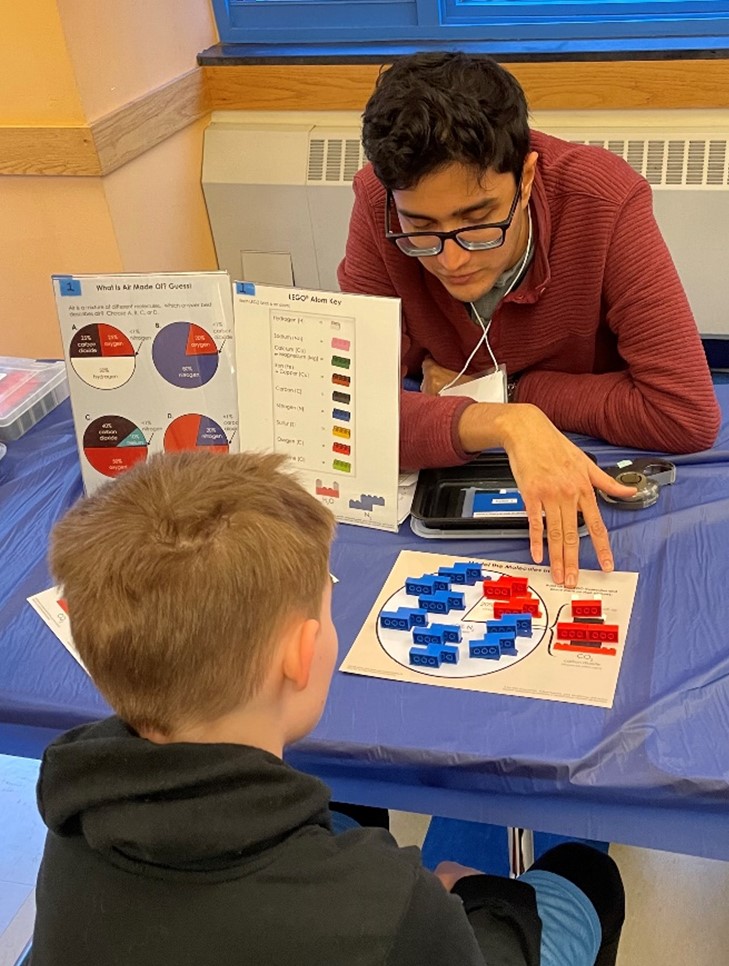
A key goal of the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) is to train future generations of scientists - in the lab and in the community. SRP Centers across the country have been doing just that, participating in community events to teach school-aged children about science.
Outreach and Community Engagement - May 9, 2023
Social psychologist Irene Lafarga Previdi, Ph.D., is dedicated to understanding environmental exposures among Puerto Rican communities, and to sharing scientific findings in understandable terms.

Outreach and Community Engagement - April 27, 2023
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded scientists from across the country gathered in person for the 2023 Society of Toxicology (SOT) Annual Meeting to share their research and exchange ideas. Held March 19 - 23 in Nashville, Tennessee, the 62nd SOT meeting and ToxExpo drew more than 5,000 attendees who gave more than 2,000 presentations and participated in more than 70 sessions.

Science Highlights - April 27, 2023
Climate change is fueling longer wildfire seasons, leading to more frequent and intense fires that could have disastrous consequences for human health. In a recent study, researchers from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC) SRP Center explored the biological mechanism behind heart and lung responses to wildfire smoke.

Outreach and Community Engagement - April 1, 2023
SRP-funded researchers created Mi PROTECT (Spanish for My PROTECT ), a mobile application to communicate environmental exposure results to pregnant people residing in a highly polluted area in Puerto Rico. The application provides information in both English and Spanish to individuals participating in studies conducted by the Northeastern University Puerto Rican Testsite to Explore Contamination Threats (PROTECT) SRP Center.

Paper of the Month - April 1, 2023
By analyzing DNA from people of different ancestries, researchers at the Columbia University SRP-Center and collaborators identified several inherited genetic variants that could influence individual sensitivity to arsenic exposure. The findings point to potential biological mechanisms underpinning arsenic toxicity.

Science Highlights - April 1, 2023
A diet rich in fiber may decrease disease risks associated with perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) exposure, according to researchers at the University of Kentucky SRP Center.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - March 29, 2023
Artist Mallery Quetawki combines her visual art skills, biology and healthcare background, and Indigenous knowledge to improve environmental health literacy among American Indian Tribes. A member of the Pueblo of Zuni Tribe in New Mexico, Quetawki has collaborated on environmental health outreach projects using art with the University of New Mexico (UNM) SRP Center. She currently serves as the artist-in-residence for the UNM College of Pharmacy s Community Environmental Health Program (CEHP).

Grant Recipient Spotlights - March 23, 2023
Upal Ghosh, Ph.D., explores how chemical contaminants move through the environment and affect aquatic food webs, with the goal of developing and implementing technologies to help ecosystems recover from pollution.

Science Highlights - March 3, 2023
Researchers at the University of Rhode Island SRP Center and collaborators revealed a link between developmental per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and reduced bone density in childhood and adolescence.

Science Highlights - March 3, 2023
For the past two decades, researchers with the University of Arizona SRP Center have been studying human exposures to mining waste and how to improve site remediation in the Southwest.

Paper of the Month - March 1, 2023
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill SRP Center uncovered complex interactions between exposure to arsenic, body weight and composition, and indicators of type 2 diabetes in Diversity Outbred (DO) mice. DO mice better capture the genetic diversity of human populations, which may help explain differences in susceptibility to arsenic-induced disease.

Paper of the Month - March 1, 2023
Dietary fiber may protect against metabolic and liver diseases related to perfluorooctoane sulfonate (PFOS) exposure, according to research by the University of Kentucky SRP Center.

Outreach and Community Engagement - February 21, 2023
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC) SRP Center adapted an existing environmental justice index to characterize toxic metals from North Carolina drinking water wells.

Paper of the Month - February 6, 2023
Researchers at the Columbia University SRP Center found that higher proportions of people belonging to racial and ethnic minorities in the U.S. are associated with significantly higher arsenic and uranium concentrations in their drinking water compared with non-Hispanic White residents.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 6, 2023
Joseph Hamm, Ph.D., strives to contribute to a deeper, fuller understanding of trust, one that crosses disciplines and helps different groups to work collaboratively toward better outcomes for community health and safety.

Outreach and Community Engagement - February 6, 2023
Short, fun science videos produced by SRP trainees as part of a competition made their big-screen debut at the SRP Annual Meeting, held December 14-16 in Raleigh, North Carolina. SRP hosted the contest to encourage early-career researchers’ science communication efforts.

Paper of the Month - February 6, 2023
SRP-funded researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill developed a computer-based approach to group wildfire exposure conditions based on their effect on genetic expression and potential health risks.

Paper of the Month - February 6, 2023
Cell-based experiments can provide relevant estimates of trichloroethylene (TCE) and tetrachloroethylene (PCE) metabolism in humans and associated health risks, found researchers at the Texas A&M University SRP Center.

Outreach and Community Engagement - January 1, 2023
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded grantees organized a workshop to discusses ways to reduce human exposure to toxic elements in food. Sponsored by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) the event focused on several themes: toxic element uptake and accumulation in plants; metal-soil interactions and cleanup; and food production and processing.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - January 1, 2023
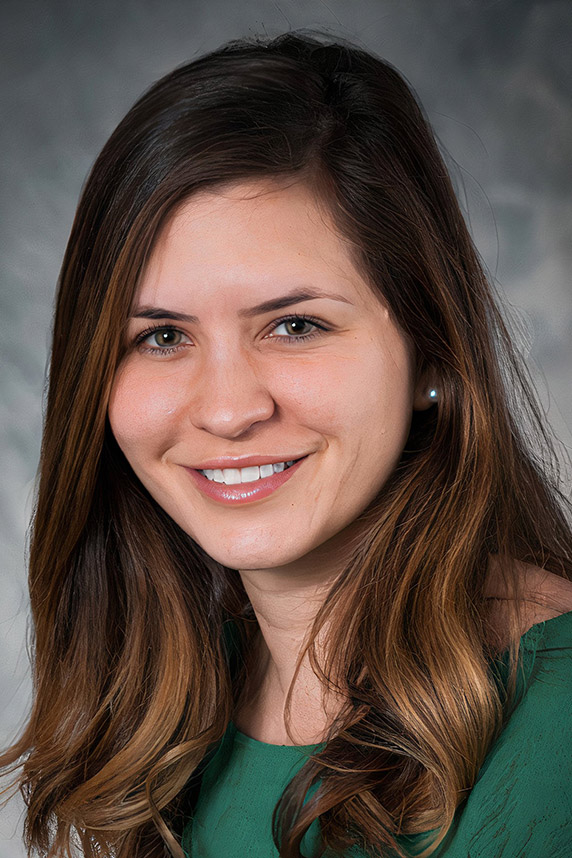
Amanda Armijo, D.V.M., Ph.D., of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology SRP Center, was selected as the 25th recipient of the Karen Wetterhahn Memorial Award. Armijo received the award December 15 at the SRP Annual Meeting in Raleigh, North Carolina, where she was recognized for her work on tracing how the toxin NDMA damages genes, and how the DNA might repair itself.

Science Highlights - January 1, 2023
Following the discovery of high levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the blood of GenX Exposure Study participants, researchers are working quickly to report their findings back to the North Carolina communities and address their concerns.

Outreach and Community Engagement - January 1, 2023
The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) marked its 35th anniversary December 14-17, 2022, at its first in-person annual meeting since 2019. Researchers, trainees, and community partners from across the U.S. gathered in Raleigh, North Carolina, to learn about select SRP-funded projects through workshops and presentations.

Paper of the Month - January 1, 2023
Adding bacteria that can break down polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) to contaminated sediments reduced the release of the chemicals into surrounding air, according to researchers at the University of Iowa SRP Center. PCBs are a family of more than 200 structurally similar chemicals that have been linked to a range of adverse health effects, including some cancers.

Outreach and Community Engagement - January 1, 2023
Strategies to move environmental cleanup technologies from research and development to the field headlined the agenda of the first in-person Federal Remediation Technologies Roundtable (FRTR) meeting in three years. The event brought together leaders from 10 federal agencies, including NIEHS, to discuss how they can collaborate to meet hazardous waste contamination cleanup goals and emerging needs.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - December 7, 2022
From a very early age, Jamaji Nwanaji-Enwerem, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.P., a former NIEHS SRP-funded postdoctoral fellow, knew he wanted to pursue a career addressing health disparities in the U.S. and abroad.

Outreach and Community Engagement - December 7, 2022
Community stories about pollution were found to overlap the locations of a burn facility s smoke plume, helping SRP-funded scientists improve their exposure assessment technique.

Paper of the Month - December 1, 2022
North Carlina State University SRP Center researchers found that American alligators living in North Carolina’s Cape Fear River had elevated levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in their blood and associated signs of immune dysfunction.

Outreach and Community Engagement - December 1, 2022
During the last two sessions of the three-part SRP Climate Change and Health webinar series. researchers discussed how climate change can potentially increase exposures to health hazards, as well as what they are doing to tackle this complex challenge. Topics covered include harzadous exposures related to hurricanes, wildfires, and melting permafrost.

Outreach and Community Engagement - December 1, 2022
Rick Woychik, Ph.D., director of NIEHS and the National Toxicology Program, traveled to Texas A&M University (TAMU) SRP Center October 27-28 for an event celebrating the renewal of TAMU’s SRP Center P42 grant.

Paper of the Month - December 1, 2022
Microbes in the human digestive system may complement a person’s ability to metabolize arsenic, particularly in the first few weeks of life, according to a Dartmouth College study funded partly by SRP. The association appears to be stronger for infants delivered by caesarean, the team found.

Outreach and Community Engagement - November 3, 2022
University of Kentucky (UK) Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center staff are teaching Kentucky residents to educate their communities about good nutrition and environmental stewardship. Staff members recently led two train-the-trainer events introducing tools and curricula for teaching adults and children.

Science Highlights - November 1, 2022
Current research on climate change and environmental health, as well as strategies to make ecosystems and communities more resilient to climate-related events, headlined the agenda of the first session of the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) Climate Change and Health webinar series, held Oct. 7.

Outreach and Community Engagement - November 1, 2022
The 19th International Conference of the Pacific Basin Consortium for Environment and Health, held Aug. 29 to Sept. 1 on Jeju Island, South Korea, brought together global experts to discuss advancing environmental health and translating scientific knowledge to action under a changing climate.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - November 1, 2022
During an NIEHS lecture Oct. 6, Elana Elkin, Ph.D., a former NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) trainee and recipient of the 2019 Karen Wetterhahn Award, described how a chemical called trichloroethylene (TCE) can interfere with fetal development in the womb.

Science Highlights - October 1, 2022
Current breast cancer research and efforts to evaluate how combined exposures can influence the disease were discussed during an NIEHS-led event Aug. 24-25.

Paper of the Month - October 1, 2022
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill SRP Center uncovered the biological mechanisms by which exposure to wildfire smoke harms the heart and lungs in mice. Wildfires are growing in intensity and frequency, posing a threat to public health worldwide. Although evidence links wildfire exposure with cardiopulmonary effects, the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown.

Paper of the Month - October 1, 2022
Researchers funded by NIEHS found that newborn mice can be exposed to the antibacterial chemical triclosan through breastmilk, leading to increased liver disease risk. According to the authors, these findings are relevant because liver disease in children is escalating in the U.S., with a limited mechanistic understanding.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - October 1, 2022
Seven trainees with the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) have earned K.C. Donnelly Externship Award Supplements. Named for longtime SRP grantee Kirby K.C. Donnelly, the funding enables graduate students and postdoctoral researchers to learn techniques relevant to their work from experts at outside institutions.
Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 27, 2022
The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) welcomes 11 new and returning multiproject centers.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 20, 2022
SRP summer interns Anna Kremer and Kirsten Reid presented their summer research projects in a virtual poster showcase along with interns and trainees from across NIEHS on July 28.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 9, 2022
Andres Cardenas, Ph.D., of the University of California (UC), Berkeley SRP Center explained how is applying his epigenetics expertise to investigate how environmental exposures contribute to the development of diseases, and how to prevent them.
Science Highlights - September 8, 2022
Funded by SRP, a study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego found evidence that newborn mice can be exposed to the antibacterial chemical triclosan during lactation, resulting in significant fat build up in their liver — an early sign of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).

Science Highlights - September 6, 2022
A novel technology that can efficiently bind to and break down per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the environment was developed by scientists at Texas A&M Agrilife Research with support from an SRP individual research grant.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 5, 2022
For nearly three decades, Johnnye Lewis, Ph.D., has advanced Native American health by combining basic research, population-level studies, clear science communication, and robust partnerships with tribes.

Paper of the Month - September 2, 2022
Researchers funded by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill SRP Center identified understudied chemicals that frequently occur in the same products as those linked to breast cancer.

Paper of the Month - September 1, 2022
Increased flooding from climate change in the U.S. will likely expose more people to legacy waste from former industrial sites, according to an SRP-funded study at Brown University.

Outreach and Community Engagement - August 24, 2022
SRP Director William Suk, Ph.D., and Health Scientist Administrator Heather Henry, Ph.D., reflected on 35 years of SRP during a conversation with NIEHS Director Rick Woychik, Ph.D.

Outreach and Community Engagement - August 17, 2022
Elizabeth Shapiro-Garza, Ph.D., director of the Community Engagement Core at the Duke University SRP Center , and Veronica Carter, with the North Carolina Coastal Federation discuss the “Stop, Check, Enjoy!,” campaign in an NIEHS podcast.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - August 10, 2022
Joel Meyer, Ph.D., of the Duke University SRP Center, discussed his research into how early-life mitochondrial toxicity can affect later-life health, during his NIEHS Keystone Science Lecture.

Outreach and Community Engagement - July 18, 2022
Researchers across three SRP-funded universities and their stakeholders organized the North Carolina Fish Forum in 2019.

Science Highlights - July 15, 2022
Researchers at the University of Kentucky SRP Center created new membranes that can deactivate SARS-CoV-2 on contact, preventing the spread of COVID-19.

Outreach and Community Engagement - July 11, 2022
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) were front and center during the 3rd National PFAS Meeting in Wilmington, North Carolina.

Paper of the Month - July 8, 2022
Prenatal exposure to chemical mixtures worsens working memory in adolescents, according to research by the Harvard School of Public Health SRP Center.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - July 1, 2022
Karletta Chief, Ph.D., of the University of Arizona SRP Center, explained how her interest in water stemmed from growing up within Navajo nation.

Outreach and Community Engagement - June 17, 2022
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) grantees developed publicly available courses to help their trainees and the broader environmental health sciences research community develop data science skills.

Paper of the Month - May 19, 2022
An SRP-funded study in mice showed that prenatal exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) altered DNA methylation in both the placenta and fetal brain in a manner consistent with neurodevelopmental disorders. The research was conducted at the University of California, Davis SRP Center.

Paper of the Month - May 19, 2022
Over the last three decades, tropical cyclones in the U.S. were associated with higher death rates in subsequent months, according to a study by the Columbia University SRP Center. The study included data on deaths in U.S. counties that experienced at least one tropical cyclone between 1988 and 2018.

Science Highlights - May 19, 2022
During recent NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) Progress in Research webinars, grantees discussed innovative strategies for bioremediation — the process of using bacteria, fungi, and plants to break down contaminants.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - May 19, 2022
Kathleen Gray, Ph.D., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC) SRP Center talked about her passion for increasing understanding of environmental exposures in communities affected by contamination.

Science Highlights - May 17, 2022
NanoAffix Science, LLC developed a new portable device to detect lead in tap water in real time. The team launched its first commercial device, called NanoAquaSense, at the Water Quality Association’s Annual Convention in early April. Their technology is funded through the NIEHS Small Business and Innovation Research program.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - May 13, 2022
Environmental toxicologist Michael (Mike) Denison, Ph.D., of the University of California (UC), Davis, who was internationally known for his fundamental research on persistent organic pollutants and for developing a widely used test for detecting toxic substances in samples, died March 22 of brain cancer. A longtime grantee of the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP), Denison served as a project leader for more than 25 years.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 19, 2022
Tiffany Sanchez, Ph.D., a former trainee at the Columbia University SRP Center, reflected on her experience as a trainee working with large cohorts, or groups of participants, to understand the connections between metal exposures and disease.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 19, 2022
Stefano Monti, Ph.D., explained how he is developing computational models for environmental contaminants to predict their long-term health effects, such as cancer and metabolic disorders. Since 2012, Monti led the Bioinformatics and Molecular Modeling Core at the Boston University SRP Center.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 14, 2022
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) grantees from across the country gathered in person and virtually for the 2022 Society of Toxicology (SOT) Annual Meeting, held March 27-31 in San Diego. The meeting highlighted diverse, cutting-edge research.

Science Highlights - April 1, 2022
A new filter cartridge that is compatible with Brita pitchers can remove per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from drinking water. The Purefast cartridges from CycloPure, Inc., are based on DEXSORB+ technology, which was developed with support from an NIEHS Superfund Research Program small business innovation research grant.

Paper of the Month - April 1, 2022
Long-term exposure to polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) mixtures in school air may affect the nervous and immune systems, according to an SRP-funded study in rats.

Paper of the Month - April 1, 2022
North Carolina State University SRP Center researchers showed that pine needles can be used as a tool to monitor the presence and distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) over time.

Paper of the Month - April 1, 2022
Researchers at the Northeastern University SRP Center used a data mining approach to identify a diverse set of chemicals that may contribute to disparities in preterm birth among different populations.

Outreach and Community Engagement - March 9, 2022
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) teams have shown resourcefulness, updating existing projects and pursuing new research to address environmental health needs.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - March 4, 2022
University of Alabama at Birmingham SRP Center Director Veena Antony, M.D., described her work to improve lung health in residents near a local Superfund site.

Outreach and Community Engagement - March 1, 2022
A new online educational resource invites high school students to examine ways that humans are exposed to arsenic and how exposure might influence susceptibility to COVID-19 infection. The tool was developed by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC).

Paper of the Month - March 1, 2022
Researchers at the University of Washington SRP Center determined how changes in the gut and liver may contribute to cadmium-induced Alzheimer’s disease (AD).

Paper of the Month - March 1, 2022
University of Iowa SRP Center researchers demonstrated a robust approach for predicting exposure to arsenic and manganese using a commonly stored but often unused biological sample. As an alternative to using whole blood, their method used only the clotted erythrocyte fraction to track metal exposures.

Outreach and Community Engagement - March 1, 2022
During her Feb. 14 NIEHS Keystone Science Lecture, Monica Ramirez-Andreotta, Ph.D., shared the numerous ways she works with communities to integrate their priorities into environmental health sciences research. The University of Arizona SRP Center researcher directs Gardenroots and Project Harvest, which are citizen science initiatives that engage community members about the health of their soil, water, and plants.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - March 1, 2022
Approaches for studying airborne exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls, and helping communities reduce such exposure, were discussed by University of Iowa Superfund Research Program Director Keri Hornbuckle, Ph.D., during her February 4 Keystone Science Lecture.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 18, 2022
A feature on Dartmouth College SRP Center Director Celia Chen, Ph.D., explains how she is leveraging decades of research on Mercury to better understand how people are exposed to per and polyfluoroalkyl substances.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 17, 2022
Monica Ramirez-Andreotta, Ph.D., from the University of Arizona SRP Center, shared her experience engaging communities in science and her journey from SRP trainee to SRP researcher.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 1, 2022
Complexities of studying per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) were shared by SRP grantees and other experts during a congressional hearing. Witnesses discussed how increased research and development can better inform regulation and strengthen methods for cleaning up PFAS in the environment.

Paper of the Month - February 1, 2022
Leveraging two decades of well water data in North Carolina, investigators at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC) SRP Center reported residents are exposed to arsenic and lead above the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency standards.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 1, 2022
Cherie De Vore, Ph.D., a former trainee with the University of New Mexico SRP Center, explained how her mechanistic research on metal contaminants in the environment is grounded in her Dine identity.

Outreach and Community Engagement - January 28, 2022
New fish consumption advisories in North Carolina were developed using data collected through the NIEHS Superfund SRP Center at Duke University. The goal is to better protect the health of people who collect and eat fish from the Cape Fear River.
Grant Recipient Spotlights - January 5, 2022
The annual meeting to celebrate the 35th anniversary of the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) was held as an abbreviated virtual event December 16, 2021. Drawing over 400 attendees from across the U.S., the meeting highlighted how SRP's dedication to innovation and collaboration across scientific fields can tackle emerging challenges.

Paper of the Month - January 3, 2022
A sophisticated biosensor may provide information about polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon distribution and potential toxicity in the aftermath of natural disasters, according to an SRP-funded study. By rapidly characterizing and prioritizing samples for study, the tool supports disaster research response where time and resources are limited.

Paper of the Month - January 3, 2022
Working with citizen-scientists, University of Arizona SRP Center researchers demonstrated that leaves can be used as a low-cost, reliable method to assess the level of metals in airborne dust.

Paper of the Month - January 3, 2022
Bacteria in the gut of young children may relate to behavioral disorders, affecting girls and boys differently, according to an SRP-funded study at the Dartmouth College SRP Center. This is one of the first studies to examine associations between the microbiome and a broad range of behavioral outcomes that may vary by sex.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - January 1, 2022
The NIEHS Superfund Research Program bestowed the honor on Molly Frazar, from the University of Kentucky.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - December 17, 2021
Duke SRP Center Co-Director Heather Stapleton, Ph.D., described her research to understand the harmful chemical exposures that people may encounter in their homes and how they affect health.

Science Highlights - November 22, 2021
Researchers at the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center at North Carolina State University (NCSU) are exploring connections between exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and immune function in both animals and humans. They are gaining insight into how exposure to PFAS over decades may harm the immune system and the body's ability to fight off infections, including COVID-19.

Outreach and Community Engagement - November 4, 2021
Approximately 500,000 Native Americans live within three miles of a Superfund site. The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) has long supported community-engaged research with Native American communities to identify strategies to reduce exposures and protect their health. To celebrate Native American Heritage Month, this article recognizes how some SRP researchers address community concerns in Tribal lands.
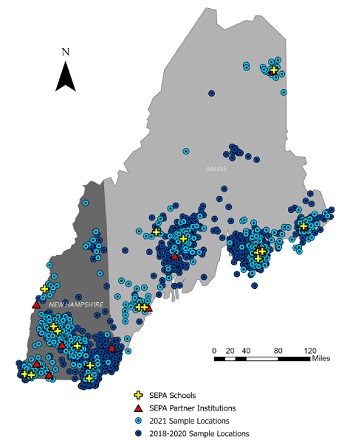
Outreach and Community Engagement - October 21, 2021
Researchers at the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded Center at Dartmouth College and collaborators quickly identified challenges and realistic solutions for their citizen science project, All About Arsenic, during the COVID-19 pandemic.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 29, 2021
Juan Parras described his partnership with the SRP Centers at Texas A&M University and the Baylor College of Medicine through the Texas Environmental Justice Advocacy Services (t.e.j.a.s.).

Outreach and Community Engagement - September 28, 2021
NIEHS-funded Brown University Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center researchers and Narragansett Tribal leaders, long-time partners in community activities, joined forces again. Through their collaboration, they are educating and empowering Tribal members to address their environmental health concerns in a way that connects cultural and scientific knowledge.
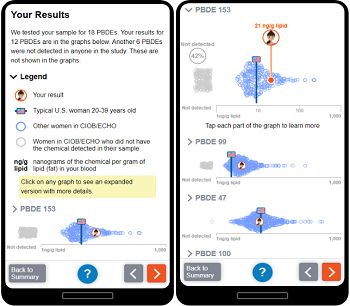
Outreach and Community Engagement - September 2, 2021
Involving the community is valuable when adjusting clinical and public health guidance, especially as it relates to the health effects of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and other chemicals of concern.

Outreach and Community Engagement - August 19, 2021
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) trainees from institutions across the Southeastern U.S. gathered virtually for a two-day event, Aug. 2 and 4, to discuss best practices for partnering with communities vulnerable to environmental exposures. The event was organized by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC), North Carolina State University, Duke University, University of Kentucky (UK), University of Louisville, and University of Alabama at Birmingham SRP centers.

Outreach and Community Engagement - August 5, 2021
Researchers from the NIEHS-funded University of Washington (UW) Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center found new evidence that environmental contamination from a former smelter in Ruston, Washington may pose a threat to human health in surrounding areas. Before publishing the results, the team reached out to coordinate risk communication strategies with agency partners and share the findings with potentially affected communities.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - July 21, 2021
When in-person events, classes, and research activities were put on hold due to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded trainees got creative and identified unique opportunities to pursue safely during the pandemic. With support from their mentors, SRP trainees gained experience across multiple scientific fields, conducted research in a collaborative environment, and engaged with diverse stakeholders and community members.
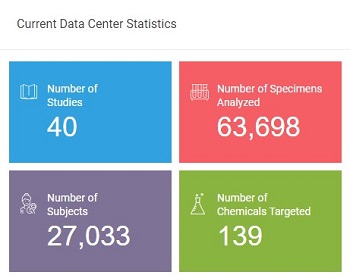
Science Highlights - July 16, 2021
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded researchers from all over the country tuned in for the Human Health Exposure Analysis Resource (HHEAR) June 2021 Virtual Grantee Meeting. The event was hosted by the HHEAR Coordinating Center and the NIEHS Exposure Science and the Exposome Webinar Series.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - June 22, 2021
Former Oregon State University (OSU) SRP Center trainee Diana Rohlman, Ph.D., discussed creative approaches for culturally sensitive community engagement and research translation.

Outreach and Community Engagement - June 9, 2021
Researchers funded by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) have been in the spotlight recently for their work on environmental justice (EJ). From being selected for prestigious committees to supporting webinar series, SRP grantees and their partners are addressing the challenges and complexities of EJ.
Science Highlights - May 10, 2021
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center uncovered a mechanism that may explain how N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) can lead to DNA damage and cancer in mice.

Science Highlights - April 27, 2021
The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) welcomes 10 newly funded individual research projects. They are incorporating new advances in materials science to optimize bioremediation of contaminants in soil, sediment, or water. Bioremediation is a cost-effective, energy efficient approach involving bacteria, fungi, and plants to break down and remove hazardous substances from the environment. These projects may offer new breakthroughs to advance sustainable solutions for hazardous substances in the environment.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 19, 2021
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded researchers from all over the country tuned in for the virtual 2021 Society of Toxicology (SOT) Annual Meeting and ToxExpo on March 16-26. More than 60 SRP project leaders and trainees from more than 13 SRP Centers gave oral and poster presentations.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 8, 2021
In an NIEHS virtual symposium, held February 23-24, NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) grantees were well represented within the broader NIEHS community, sharing their efforts to understand the relationship between environmental exposures, the microbiome, and human health.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - April 7, 2021
Angela Gutierrez, Ph.D., of the University of Kentucky SRP Center shared her journey from SRP trainee to NIEHS small business innovative research grant to develop new strategies to remove contaminants from water.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 5, 2021
Rachel Morello-Frosh, Ph.D., conducts research to understand how social factors, such as inequality and psychological stress, interact with environmental chemical exposures to influence disparities in the health status of different groups.
Grant Recipient Spotlights - February 1, 2021
Two workshops, held December 16 as part of the first NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) virtual annual meeting, provided forums to delve into data science issues and showcase innovative remediation and detection technologies.

Science Highlights - January 10, 2021
In a new study, funded in part by the NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP), researchers improved an approach to remove persistent organic pollutants (POPs) from foods of animal origin. Michael Denison, Ph.D., from the University of California, Davis SRP Center collaborated with a team of researchers from the European Union Reference Laboratory to test several laboratory methods and develop an improved method for the extraction of lipids and associated POPs bound to animal tissue.

Science Highlights - January 6, 2021
NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) small business grantee OndaVia, Inc. successfully implemented their water analysis system at the NIH campus in Bethesda, Maryland. The system uses spectroscopy and nanotechnology to provide instrumentation for rapid, on-site, easy to use, and inexpensive laboratory-grade testing of chemicals in water.
Outreach and Community Engagement - December 9, 2020
The NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP) provided supplemental funding to four centers to expand the focus of their research to address critical knowledge gaps related to exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus and its disease, COVID-19. In response to the evolving nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, this funding encourages SRP researchers to address the public health crisis and its disparate effects on vulnerable populations.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - October 9, 2020
Michael (Mike) Aitken, Ph.D., professor emeritus of Environmental Sciences and Engineering at the University of North Carolina (UNC) at Chapel Hill, passed away September 19 after a long, courageous battle with cancer. Aitken served as a project leader and integral part of the UNC Superfund Research Program (SRP) Center for more than 20 years.
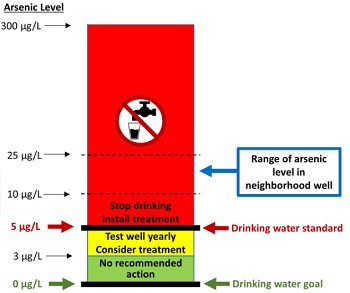
Science Highlights - October 1, 2020
In a pair of recent publications, researchers from the Columbia University SRP Center demonstrated a strategy to improve private well testing for arsenic. They also showed that water treatment systems effectively reduced arsenic water levels and may reduce the likelihood of developing cancer.
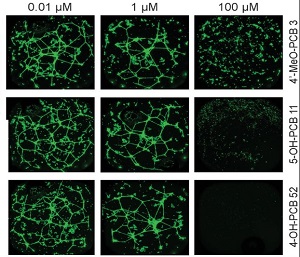
Science Highlights - September 3, 2020
A new NIEHS Superfund Research Program (SRP)-funded study demonstrated a strategy using data from cell studies to characterize how exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) may harm human health, particularly the cardiovascular system. PCBs are a large and complex group of chemicals that often occur in mixtures and can contaminate soil, groundwater, and air.

Grant Recipient Spotlights - September 3, 2020
A new virtual seminar series is providing an opportunity for researchers to share information on per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). The first session of the series, which kicked off on July 31 and included more than 400 participants, featured Angela Slitt, Ph.D., of the NIEHS-funded University of Rhode Island Superfund Research Program Center.


